 The panel of system properties is one of the most important parts of Windows, always present since the first editions. Even if that of the system properties is one of the main parts of the Windows system and also one of the most complex and delicate, which you should understand and know to be truly masters of your computer.
The panel of system properties is one of the most important parts of Windows, always present since the first editions. Even if that of the system properties is one of the main parts of the Windows system and also one of the most complex and delicate, which you should understand and know to be truly masters of your computer.Most Advanced settings present in System Properties are certainly not things you need to change often and, in most cases, you should probably leave the default ones, but it is very useful to understand them and know what you can do from that control panel.
NOTE: Do not confuse the Windows system settings with the completely different Windows 10 settings.
UPDATE: See here how find System Settings in Windows 10, where the classic Control Panel screen has disappeared.
To open the Advanced system settings in Windows 10 and Windows 8 just press the right mouse button on the Windows flag at the bottom left and click on System.
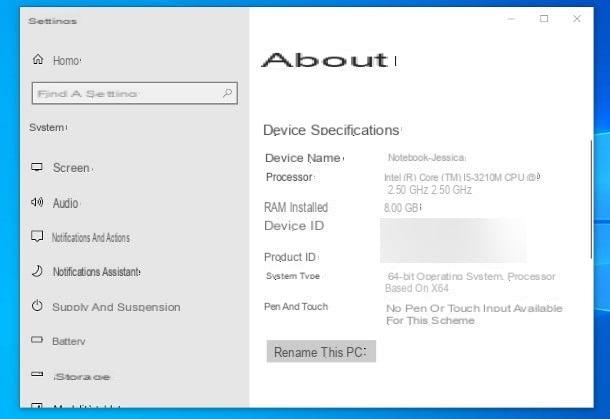
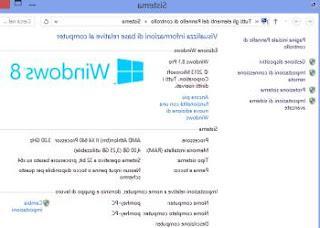
If you are using Windows 7 you must first go to the Control Panel and search for System or you can right-click on Computer and then choose the properties. Although it may seem strange, the window that opens is almost purely informative about the computer you are using.
In another article we saw how to change computer information: manufacturer, model, logo ....
However, you have to click on Advanced settings to enter the real property panel. Among the various cards, that of Advanced it is the most interesting, the one in which you can change the configuration of the computer by making important changes. The tab is divided into four sections: performance, user profiles, startup and recovery, and environment variables. The average user wouldn't really need to change anything here, except in some very common circumstances.
Then press on Settings under the heading Performances to decide which visual effects to enable and which to disable. The visual effects they are also beautiful to look at, but they consume a lot of memory and make the computer slower.
You can then choose to set them for the best performance or follow this guide on how to have Windows 7 super fast by changing unnecessary options. For example, I always disable the annoying animation to minimize windows.
The performance sheet is divided into three sheets including, again, that of Advanced very important. From here you can change the size of the paging file, the amount of disk space to dedicate to virtual memory. On older and less powerful computers it is (rather was) useful to change this amount or disable it completely as explained in the guide on setting up the Windows virtual memory or paging file. With modern PCs using 4GB of RAM or more, the pagefile loses its importance and can be left as it is.
Additionally, Windows 7 and 8.1 only use the paging file when really needed and are much smarter than XP in this regard.
It tells us that you can usually disable the paging file in computers with a lot of RAM, but it is not recommended because some programs may need it and would crash if not found.
For the other option concerning the how processor resources are allocated you should leave it in Programs and choose to get better performance for services only if your computer is a server.
In the third tab we have the program execution protection that it is not clear what it means.
This protection, called Data Execution Prevention (DEP), is available in 64-bit versions of Windows and prevents virus applications from exploiting parts of memory for their own malicious purpose. Obviously it should never be disabled (it can only be disabled using tweaking programs) and you can leave the protection active only for essential Windows programs and services. If you want to check which processes are protected by this function, you can open the task manager, go to "details", right-click on the column header, click on Column selection and add that of DEP .
Returning to the Advanced system settings, on the Advanced tab, after the performance you can click on System settings User Profiles. The User Profiles function is not very useful for home use of the computer, it is especially useful for creating common profiles in a Windows domain.
Le Startup and Reset settings They have two useful features for a dual-boot computer, to choose the default operating system and to change the length of time the choice menu is displayed. You can also choose whether to automatically restart Windows after a blue screen crash and to write information about the cause to a memory dump file. Disabling automatic restart is useful for taking the time to write down the error message.
Le environment variables are common settings for applications, to quickly launch specific programs from the Run box.
We have seen in another article how to change the TEMP and TMP environment variables on Windows to move temporary files by explaining roughly what they are and how they are used.
Returning to the system settings window, going beyond the Advanced tab we have:
- Protection, where there is system restore already explained in another guide. Take into account that on Windows 8.1 there are other options to reset or reinitialize Windows 8 and that in Windows 10 there is a reset
- The board Remote connection it is very simple and only allows you to choose whether or not to enable Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop (only in Windows Professional). If these features are not used, they must be disabled. While useful, it's much easier to use programs like Teamviewer or Chrome remote desktop for the remote desktop.
- Change Name on PC it can be nice but useless, unless you have an internal computer network.
Computer name and Workgroup are important for creating a computer LAN at home or in the office and for sharing files and printers.
The computer description is completely useless while the network ID should only be entered in the case of a Windows domain.
- Hardware finally, it is a tab with two important buttons: one to access the device manager, the other to decide how to install future driver updates downloaded from Windows Update, whether with an automatic or manual procedure.
READ ALSO: "Computer Management" administrative tools in Windows
System Settings Guide in the Windows Control Panel