What is the barcode and what is it for
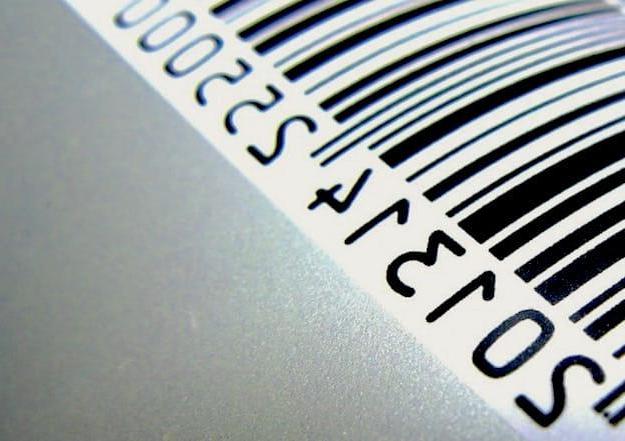

Let's get right into the topic and see what is the barcode and what is it for. Basically, the barcode is a identification code consisting of a set of high-contrast graphic elements that can be read through a scanning sensor (but also with the camera of a smartphone) and decoded to read the information it contains.
Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver, two engineering students of the University of Drexel, developed the idea of the barcode, but in reality the diffusion of this technology did not happen before June 26 1974, the date on which the first product with a bar code was sold: a packet of chewing-gum ("artifact" that can still be seen today at the Smithsonian's National Museum of American History).
But how do you read a barcode? The most reliable technology employs a laser beam reader, usually paired with a oscillating head and sometimes to a mirror system, which increase the accuracy of the reader itself. Cheaper readers, on the other hand, use one LED bar to illuminate the barcode and a CCD sensor (Charged Coupled Device).
In some areas, such as those connected with some industrial sectors, a technology of capturing an image provided by a video system which, with the help of suitable software, allows you to take a photograph of the product on which the barcode is applied and recognize, read and interpret the code itself.
Given the practicality of using the barcode, it is not surprising that it is used in various areas. In addition to the sector of sale of products of various kinds, it is widely used in Publications And in the periodicals (in order to facilitate the identification and classification of the same), in transport to identify the trains in transit in some railway sections and in the underground lines, in the fidelity cards and even for reading some identity documents, such as the health card and the tax code.
There are two large families of barcodes: those linear or one-dimensional (1D) which systematically represent the data, varying lengths and spacings between multiple parallel lines and those two-dimensional (2D), which represent data in a systematic way, using 2D symbols and shapes. They have similar characteristics to linear barcodes, but can contain much more information.
Among the linear barcodes most common in our country, according to regulations currently in force, we find the EAN code (European Article Number), used in large-scale distribution; the Pharmacode, used for drug identification; L'Universal Product Code used to mark products imported from the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand. An example of two-dimensional barcodes, on the other hand, they are i QR code (of which I have extensively told you in this other guide).
Codes consist of spazi e black areas (The bars precisely). By space we mean the clear element of the code, which separates two bars from each other (the black elements). Each code also has one or more modules, which is the width of the narrowest element (bar or space). As I told you, it is thanks to these spaces that readers are able to read barcodes and decipher the information they contain. Later I'll explain how you can read them through dedicated apps and devices.
How to read barcode
After analyzing, in broad terms, the technology behind the functioning of the barcodes, the time has come to see how to read the codes in question.
Below you will therefore find explained how to read barcode through convenient apps for smartphones and tablets and through hardware code readers used for the purpose, more precise and faster.
QR & Barcode Scanner (Android/iOS/iPadOS)

One of the best barcode reading apps is QR & Barcode Scanners. As easily understood from its name, it is a solution that is able to read not only barcodes but also QR codes. It is available for free download for Android (from the Play Store or from alternative stores) and iOS / iPadOS. Please note that its free version features (non-invasive) advertising banners that can be removed by purchasing the full version, which costs € 4,49.
After installing and launching the QR & Barcode Scanner, grant the app permission to access the camera of the device on which you have installed it and accept the conditions of use of the service by pressing the button Accept (this is only necessary on Android).
Later, if you use the version for Android of the app, frame the barcode of your interest and, when this is captured by the app, press the button Search for product, Search book o Search for content (based on the type of product on which the code is applied), so as to see what lies behind the code itself. Pressing on the button Shareinstead, you can share the code that has been read through the available options.
If you use the version for iOS / iPadOS QR & Barcode Scanner, on the other hand, after making sure that the item is selected Scan (top left), frame the code of your interest. Then press the button Procuct search if the code is attached to a product, Web search if it relates to web content or Book Search if it's about a book. To share it, instead, tap on the item Share and select one of the sharing options from those available.
Other apps to read barcode

In addition to the one mentioned in the previous chapter, there are many other apps to read barcode. Below you will list some that might be right for you.
- ScanPro (Android / iOS / iPadOS) - is a very powerful document scanner that, if necessary, can also be used for reading bar codes and QR. Basically it is free, but the advanced functions are available by subscribing to a subscription, which starts at € 6,49 / month.
- Barcode Scanner (Android) - it is a free app based on the ZXing open source libraries through which you can scan barcodes and QR codes in a simple, fast and free way.
- Onlinebarcodereader.com (Online) - it is a Web application through which it is possible to read barcodes (and not only) by uploading the image that contains them or by specifying the URL of the latter.
For more information on how to use these and other barcode reading apps, I refer you to the reading I have dedicated to the latter.
Bar code reader

As I told you earlier, there are also devices that act exclusively as barcode readers. How do you say? You are very intrigued by the latter and, therefore, you would like to know how a barcode reader works? I try to explain it to you briefly.
Well, these devices usually use a laser (or similar technology) to "read" the alternating lines and blanks in barcodes. Then they send the collected data to a decoder which, after analyzing them, translates them into information and data, according to the standard used.
Depending on the model of player purchased, after connecting it to the USB port of your computer, it may be necessary to download drivers from the manufacturer's website or a client that allows it to function correctly. If you want, you can find more information on the website of the manufacturer of the reader that you will eventually purchase (or with a simple search on Google).
There are various types of barcode readers on the market. In essence, however, they are divided into three major categories.
- Laser readers - it is the most popular type of reader and, probably, it is what you thought about before coming to this guide. This type of reader uses a red diode laser to read the reflectance (ie the ability to reflect light) of the black and white spaces of the barcode. They can only read standard linear barcodes (1D).
- Linear imager readers - this too is a standard 1D linear barcode reader, whose operation differs from that of laser readers, in that instead of reading the light reflected by the laser, they take an image of the barcode itself.
- 2D imager players - the operating principle of these readers is similar to that of linear imager readers, but as their name suggests, they allow you to read not only 1D, but also 2D codes. These scanners are capable of reading barcodes regardless of their position and direction, which makes them much faster than laser scanners and linear imagers.
The prices of these devices can also vary a lot. The cheaper ones cost a few tens of euros; the more advanced ones (which are also the most precise and fastest ones), on the other hand, can cost more than 100 euros. They can be found in the most well-stocked electronics stores and online stores, such as Amazon.
See offer on Amazon See offer on Amazon See offer on Amazon Barcode: how it works