What is GPS

Before going into the matter and explaining how GPS works, it is good to start from the beginning by explaining what this term means: GPS is the acronym of Global Positioning System and it is a positioning system based on satellites in orbit, capable of providing the location and exact time to any device equipped with a suitable receiver. It works at any time and regardless of the weather conditions. To be more precise, the full definition of this positioning system is NAVSTAR GPS, namely Navigation Satellite Timing And Ranging Global Positioning System.
The GPS system, designed by the US Department of Defense, was born in 1973 as a successor to the Transit system to offer the possibility for military vehicles to orient themselves in space (and time) in any position and in any weather condition. Only in 1991, however, the United States decided to open the use of GPS also to civilians, but with some limitations (which did not concern military use): for safety reasons, the signal sent by the satellites was "altered" on purpose by a particular mechanism, decreasing theorder of precision detection of civilian receivers - the detection error could reach up to 950 meters relative to its original position.
In 2000 these limitations were abolished, making the survey for civil uses much more precise: to date, the GPS survey guarantees an accuracy of 10 or 20 meters compared to the real position, certainly a good leap forward compared to what happened in the past.
Primarily, the entire GPS system consists of three "parts", or segments, who work together to offer placement in the ways I indicated earlier. Below I illustrate them all.
- Space segment - it is the constellation of satellites placed in the Earth's orbit. In total, around the earth, they orbit 31 artificial satellites (24 are active, while others become active in case of need) arranged on 6 distinct levels, which continuously emit signals on two different channels: L1 for civil use (SPS), e L2 (PPS) for military use.
- Control segment - it is the combination of 8 control stations satellites (7 operational and one "reserve"), scattered in strategic points of the Earth, together with the 4 antennas terrestrial capable of sending each satellite the necessary updates over time. The staff inside the control stations takes care of the complete management of satellites, signals and services.
- User segment - this segment is none other than the set of GPS receivers present on our planet, both military and civilian. Generally, a receiver consists of a small processor to process the operations, a GPS antenna and a time source, useful for carrying out the synchronization operation (I'll talk about it shortly).
The detection of the position via GPS is based on the principle of trilateration: using the radio signals generated from three satellites and the distance of the Earth from each of them, the receiver, thanks to the travel time of the 3 signals, is able to calculate the point of the planet in which it is located, with a fairly high precision margin, reproducing it if necessary on a digital map (as I explained before, the SPS localization has an error of less than 20 meters compared to the real position).
The clock on board the receiver, however, is not as accurate as the one on board the 3 satellites involved in the triangulation, therefore the receiver itself is not able to immediately know the exact moment in which the signal started: for this takes advantage of the signal sent by a fourth satellite, useful for "correcting" the clock on the receiver and synchronizing it with the satellite one. This is why a GPS receiver can receive at any point on earth signals from at least 5 different satellites (4 operative plus one "spare").
Before moving on, I believe it is my duty to provide you with another important information: GPS is the most used positioning system in the world, but it is not the only one. Some nations and continents, for a variety of reasons (including the fact that the space and control segments of GPS are owned by the US, a nation that could theoretically ban its use at any time), have created positioning systems alternatives: GLONASS (Russia), BeiDou/Compass (Asia), IRNSS (India) e Galileo (Europe).
What is GPS for

If you have read carefully what I have told you so far, you have certainly understood the ultimate goal of GPS: this system is capable of to locate any object equipped with a receiver, in any point on Earth and any time, regardless of the weather conditions.
As I have already explained to you, a GPS receiver is nothing more than a "chip" equipped with aAntenna, a lowercase processor and a kind of clock able to pick up the satellite signal and to detect, with the rules I explained to you a little while ago, the terrestrial coordinates of its position, eventually returning them to one map thanks to special systems, programs or apps.
The first devices equipped with a GPS chip were simple detectors with a small display on which terrestrial coordinates were shown. With the passage of time and the evolution of technology, it has become possible to use many categories of devices to take advantage of this technology: here are some of them.
- Car navigators - these are devices generally designed for navigation only using GPS technology. They are equipped with a screen, a processor, a RAM memory and a GPS chip (as well as optional components such as Bluetooth, battery, WiFi etc.), and can show entire customizable travel itineraries, as well as the current position. exploiting maps di nations o entire continents, which can be downloaded as needed. If you need a navigator, I suggest you refer to my dedicated buying guide.
- GPS tracker - these are real "locators", equipped with a GPS chip, capable of determining the position of the object to which they are connected or of the person wearing them, interfacing with special programs for computers or apps for smartphones and tablets. Some trackers are equipped with additional chips such as WiFi and Bluetooth, while others are so small that they are almost invisible: you can find a wide choice by consulting my guide to the best GPS Trackers.
- Smartphone, tablet e computer - for some time now, these commonly used devices have been equipped with a GPS chip that can be activated or deactivated as needed and used, through dedicated programs or apps, for multiple purposes ("transforming" the devices into satellite navigators or to locate them when they are lost or stolen, just to name two common scenarios). To be precise, not all computers are equipped with a GPS chip, however it is possible to take advantage of location services by using the Internet connection, combining the IP address obtained from the machine with the location of the nearest server, belonging to the manager to which it is connected.
How to use GPS
Now that you've learned the basics about how GPS works, the time has come to go to practice and activate the location systems on your smartphone, tablet or computer: below, I will explain how to activate and use GPS on Android devices, on iPhone and iPad and on your computer.
Before continuing, however, I want to clarify that the location services can be used by the programs and apps that request them, only if you grant them the access permissions to GPS - by touching or clicking on Allow o OK within the dialog boxes that will be proposed to you.
Android

You have a terminal with the operating system Android? Don't worry, activating GPS is very, very simple and you can do it either by using thenotify area that the appropriate panel within the settings.
Therefore, to activate the GPS almost immediately on Android, recall thenotify area on your smartphone or tablet, swiping from the top of the screen to the bottom, and tap the icon GPS (o Localization, depends on the operating system) present in the panel that opens: when this lights up, the GPS is active and available for the apps and services that want to use it.
Can't find the GPS icon in the Android notification area? Don't worry, you can also do the same through the system menus: first, tap the icon Settings placed on the screen of the apps installed on your device, then scroll down until you find the section personal and touches the voice Geolocation. At this point, move up ON the switch located at the top right of the proposed panel and that's it.
In some custom versions of Android, such as the MIUI di Xiaomi, the procedure may change slightly: in this case you have to open the Settings of Android, go to the section System & Device and, from there, touch the voices Additional Settings, Privacy e Geolocation, then move to On the switch at the item Access to my location.

From the same panel, you can also activate high-precision location services (I'll talk about this shortly) or check the apps that have recently accessed location services. It wasn't difficult, was it?
iOS

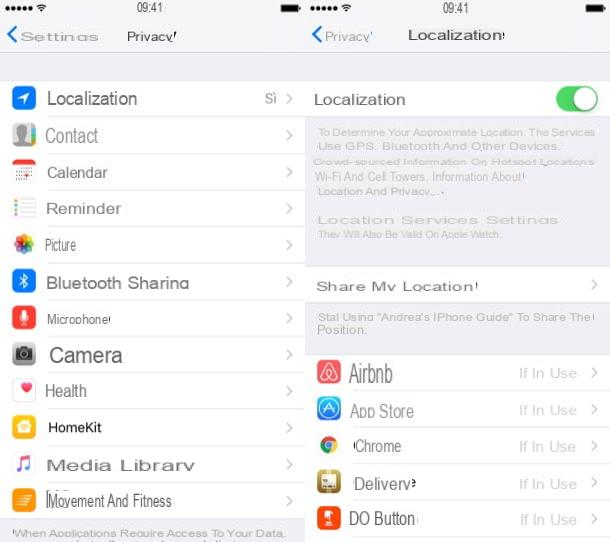
Have a iPhone or of an iPad? Don't worry, turning GPS on or off is very simple! First, tap on the icon Settings resident on the main screen of your device and select the items Privacy e Location give the menu check if you press.
Now, to "turn on" the GPS, activate theswitch located at the top right, in correspondence with the item Location And that's it! From the same panel, you can enable or disable location sharing via system apps, or revoke the access permit to apps installed on the device.
computer
So far I have told you about how to activate GPS on smartphones and tablets. What if I told you that these services can also be activated from desktop and laptop computers? Yes it can be done. Before explaining how, however, I have to make an important clarification: not all computers are equipped with a GPS chip, so it can happen that the location is also obtained using any Bluetooth devices, WiFi connection or possibly the connection via cellular modem (for example eg using the "4G Internet keys").
Having made this necessary premise, it's time to take action: if you use Windows 10 and you want to activate the GPS on your PC, click on the icon in the shape of Comics located at the bottom right of the screen, next to the clock, and click on the icon Location. If you don't see the icon in question, click on the item Expand all and you should see it appear.

If you have a Mac, activate the localization in this way: click on the icon System preference placed on the Dock, then on the icon Security and Privacy and on the section Privacy, located at the top right.
At this point, unlock the changes by clicking on the button in the shape of padlock at the bottom left, enter your password, press the button Unlock and tick up Enable "Location Services". Through the same screen, you can view all the programs that have requested and obtained access to the location.
Once the service is activated, you can tune to programs and / or Web sites permission to use GPS (or location via WiFi / Bluetooth / modem) by clicking on the button Allow that appears in the confirmation windows proposed by the operating system, or in the information panels placed immediately under the address bar of the browser Safari.

Even browsers like Google Chrome have a function to allow the detection of the geographical position by the sites and Web services used: to proceed, open the "big G" browser, press the button ⋮ collocato in alto a destra, selects the voice Settings, scroll to the bottom of the page and click on the item Advanced.
Once the next section of the page has loaded, click on the item content settings, Then Location, and move up On the switch located at the top (the voice will turn from Blocked a Ask before signing in). From this moment on, when a site wishes to access the position, a small information panel is shown at the top left: to grant access, click on the button Allow.

How to improve GPS signal reception
I have mentioned to you several times, in this in-depth study, of how the localization via GPS signal is possible at any point on the Earth, at any moment and regardless of weather conditions. However, since GPS receivers rely on a satellite signal, reception is not always optimal and, in some cases, it may take longer to obtain an acceptable result.
Do you find yourself exactly in this case? Do not despair, all is not lost: there are some small "tips" to follow for improve GPS signal reception, especially on smartphones and tablets. Below I point out the most useful ones.

- Eliminate obstacles - to better receive the signal from the satellites, it is advisable that there are no “obstacles” between the “source” (the sky) and the receiver. Consequently, I recommend that you use GPS by pointing the device straight to the sky, better if outdoors and in the absence of elements such as ceilings, partitions or other.
- High precision localization services - if the GPS alone fails to provide you with a very precise position, you can take advantage of the “high precision” location, which also uses the information received from WiFi, cellular connection and Bluetooth. To activate it on Android, go to Settings> Location, tap on the item modality and set the check mark on the item High precision. However, this step is not necessary on iOS, where "high precision" services are enabled by default.
- Use an app - in the Android and iOS stores, there are some apps that check both from how many satellites it is possible to receive information, from the current position, and the quality of the signal received, so as to allow you to find the optimal position to reach your goal. In this regard, I would like to point out the GPS Test apps for Android and GPS Status for iOS.
- Use an external antenna - if you need to use GPS in an inaccessible place, and your device just can't lock onto the signal, you may want to use an external GPS antenna. There are different types and with different connection methods, depending on the device to which they are dedicated (satellite navigator, smartphone / tablet, computer, etc.).
Now that you know all the necessary information about GPS, you can finally take advantage of this technology with the knowledge of how it works. Before concluding, however, I want to give you some advice: do not think that GPS is only for "navigation", since this small chip can also be useful if your device is lost or stolen: if the GPS is active, there is the possibility to locate the device before it is turned off or to know its last position. I told you in detail about this aspect in my guides on how to locate GPS and how to track down a stolen cell phone: I recommend that you read them carefully.
How GPS works